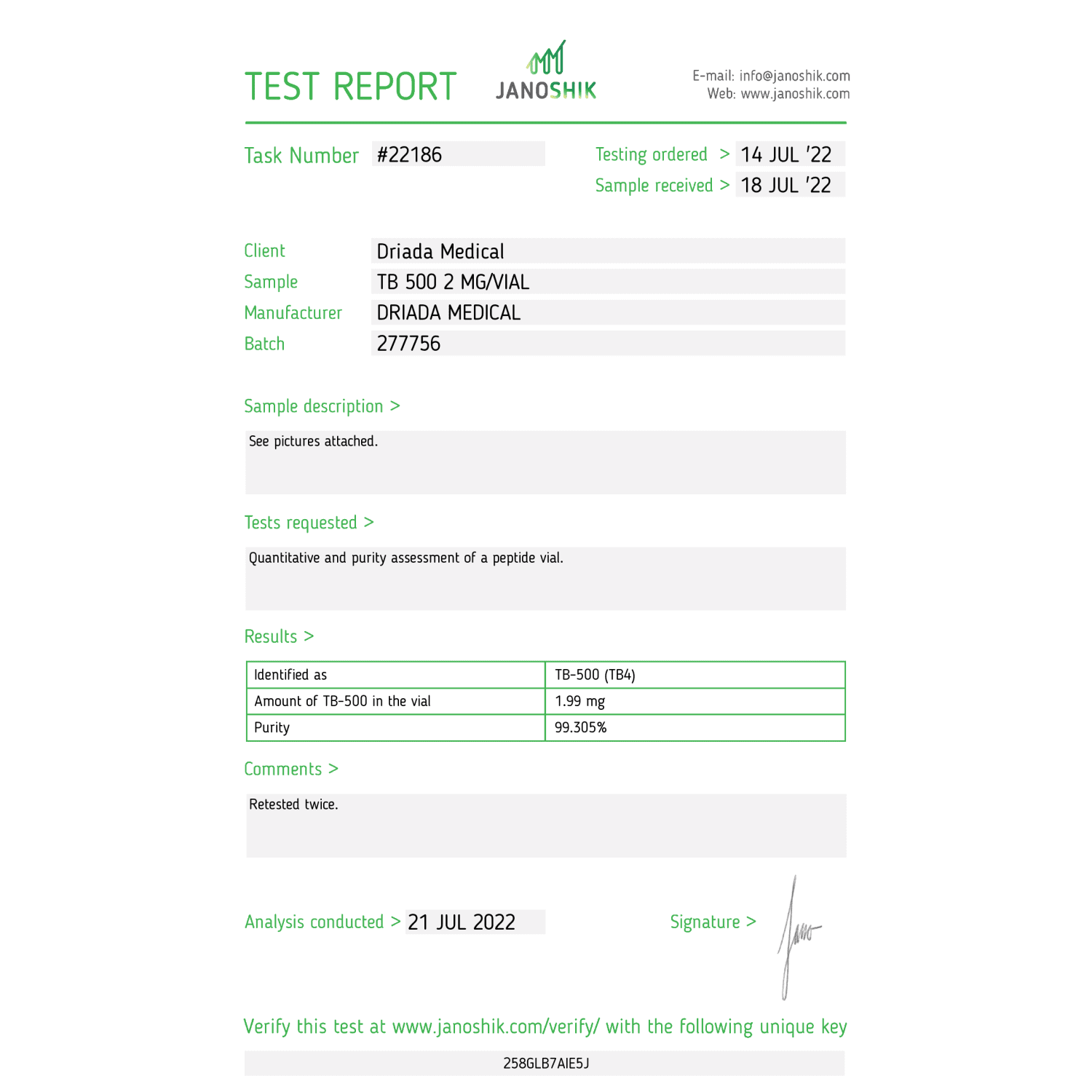
TB-500 2mg
Thymosins are small proteins found in various animal tissues, initially discovered in the thymus but now known to exist in many other tissues as well. Two specific thymosins, Thymosin Alpha 1 and Thymosin Beta 4, have shown potential medical applications and are already being used in clinical settings. Thymosin Beta 4 (TB-500) is a peptide fragment derived from the naturally occurring hormone Thymosin Beta 4. Although often marketed as Thymosin Beta 4, TB-500 is distinct from the full hormone. Thymosin Beta 4 is released by the thymus gland, which is more prominent in children and decreases in size with age, but is also produced locally in various cells. Studies have shown that Thymosin Beta 4 plays a role in wound healing, stem cell differentiation, and reducing inflammation.
Although TB-500 shares similarities and properties with Thymosin Beta 4, it is more convenient to produce. TB-500 can promote healing, improve mobility after injury, and reduce pain caused by inflammation. It has become popular among athletes and bodybuilders who see it as a way to speed up recovery after training. TB-500 is also used in the treatment of sports injuries and as a preventative measure against such injuries.
Action Mechanism
Among the thymosins, Thymosin Beta 4 is the most abundant, widely studied, and biologically active member of the beta-thymosin family. As an actin-binding peptide, Thymosin Beta 4 regulates actin polymerization, which plays a role in cell migration, angiogenesis, and tissue regeneration. It has demonstrated cardioprotective properties, stimulating angiogenesis in ischemic cardiac muscle, blocking proapoptotic cascades in cardiomyocytes, and activating survival pathways under stress. Thymosin Beta 4 is also effective in the treatment of trophic ulcers, wounds, burns, and chronic dermatitis due to its anti-inflammatory effects. It promotes blood vessel growth, influences stem cell differentiation, and has a wide range of potential therapeutic applications, attracting significant attention from researchers and the cosmetics chemical industry.
Wound Healing
Thymosin beta 4 plays a crucial role in the repair and regeneration of damaged cells and tissues. It is released by platelets, macrophages, and various other cell types following injury, protecting cells and tissues from further damage, reducing inflammation, and inhibiting microbial growth. Thymosin beta 4 binds to actin, promoting cell migration and the mobilization, migration, and differentiation of stem/progenitor cells, which contribute to the formation of new blood vessels and tissue regeneration. Additionally, Thymosin beta 4 reduces the accumulation of myofibroblasts in wounds, reducing scarring and fibrosis.
TB-500 supports the treatment of muscle, tendon, ligament, and skin injuries. It accelerates healing, reduces inflammation, and can be used for acute, slow-healing injuries or chronic, non-healing injuries. Common applications include tendinitis, muscle strains or pulls, as well as various muscle and connective tissue injuries. TB-500 also reduces the risk of pathological and interstitial adhesions, improving tissue mobility. It has demonstrated efficacy in accelerating the healing of wounds, cuts, and burns, minimizing scarring. Clinical studies conducted on patients with chronic ulcers have shown that Thymosin Beta 4 significantly accelerates wound healing and is well tolerated.
View
TB-500 is used in ophthalmology for the treatment of dry eye syndrome and neurotrophic keratopathy. Animal and human studies have demonstrated its ability to promote rapid and complete healing of damaged corneas. Patients with moderate to severe dry eye symptoms have experienced significant and lasting improvement after treatment with TB-500.
Cardiovascular System
Thymosin beta 4 has potential in regenerating human heart muscle damaged by heart attacks or other cardiac conditions. Animal studies have shown that thymosin beta 4 stimulates the formation of new myocardial cells from inactive precursor cells in the heart wall. It also promotes angiogenesis and exhibits anti-fibrotic effects, benefiting myocardial cell remodeling. The regenerative potential of thymosin beta 4 in cardiovascular disease has shown promise in several preclinical studies, and early clinical trials have evaluated its safety and efficacy in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Hair Growth
Animal studies have indicated that TB-500 can promote the development, differentiation, and migration of stem cells in hair follicles, thereby accelerating hair growth. Thymosin peptides have been proposed as agents to prevent hair loss by inhibiting the catagen phase, during which hair follicles shrink and the hair papilla “rest.” Human reports suggest that TB-500 effectively prevents hair loss and stimulates hair growth.
Nervous System
Thymosin beta 4 is present in cells of the central nervous system and is believed to play a protective role, influencing synaptogenesis, axon growth, cell migration, and brain plasticity. It has been linked to neural development, particularly of sensory neurons, and exhibits increased activity in various pathological conditions. Thymosin beta 4 improves vascular remodeling and elasticity within the nervous system, promoting neurological recovery in neurobiological diseases. Its role in regulating pro-inflammatory signaling from toll-like receptors has also been suggested.
Effects
- Accelerated healing of muscles, ligaments, joints and skin with repair potential
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Promoting angiogenesis in muscles by improving their nutrition
- Potential protective and restorative effects on the nervous system
- Stimulation of luteinizing hormone secretion and subsequent testosterone production
- Increased tissue sensitivity to insulin
- Cardioprotective properties, reducing the risk of myocardial infarction and facilitating myocardial regeneration
- Anti-inflammatory effects and positive influence on hair follicle growth
- Accelerated healing of damaged corneas in the treatment of dry eye syndrome and neurotrophic keratopathy
Side Effects
- Possible redness and pain at the injection site
Usage and Dosage
The loading phase involves a weekly dose of 2–6 mg, divided into two injections (for example, 2 mg each on Monday and Wednesday) for one month. The maintenance phase consists of 2–4 mg per week, divided into two injections, for a duration of approximately 1–2 months. An alternative dosing regimen includes a loading dose of 10 mg in the first week (1–2 mg per day), followed by 5 mg per week (divided into two injections) for five weeks. The maintenance dose is 10 mg per month (2 mg every six days) and has been found effective by many athletes using TB-500. As knowledge advances, dosing protocols may evolve.
Combination with Other Drugs
Combining TB-500 with growth hormone, GHRP, or GHRH can enhance its tissue regenerative effects. In cases of tendon injuries and bone fractures, it is advisable to add BPC-157, as the combination produces a pronounced synergistic regenerative effect.
Preparation and Storage
To prepare the solution for injection, a syringe containing the diluent is injected into the vial containing the lyophilized powder. The diluent should be added slowly to the edge of the vial, without injecting it directly onto the powder. Gently stir the solution until the powder dissolves completely, creating a clear liquid. The prepared solution can be stored in the refrigerator at 2-8°C for approximately 21 days, or longer if bacteriostatic water was used as the diluent. Avoid mixing different peptides in the same syringe to prevent degradation of the fragile peptide molecules.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.