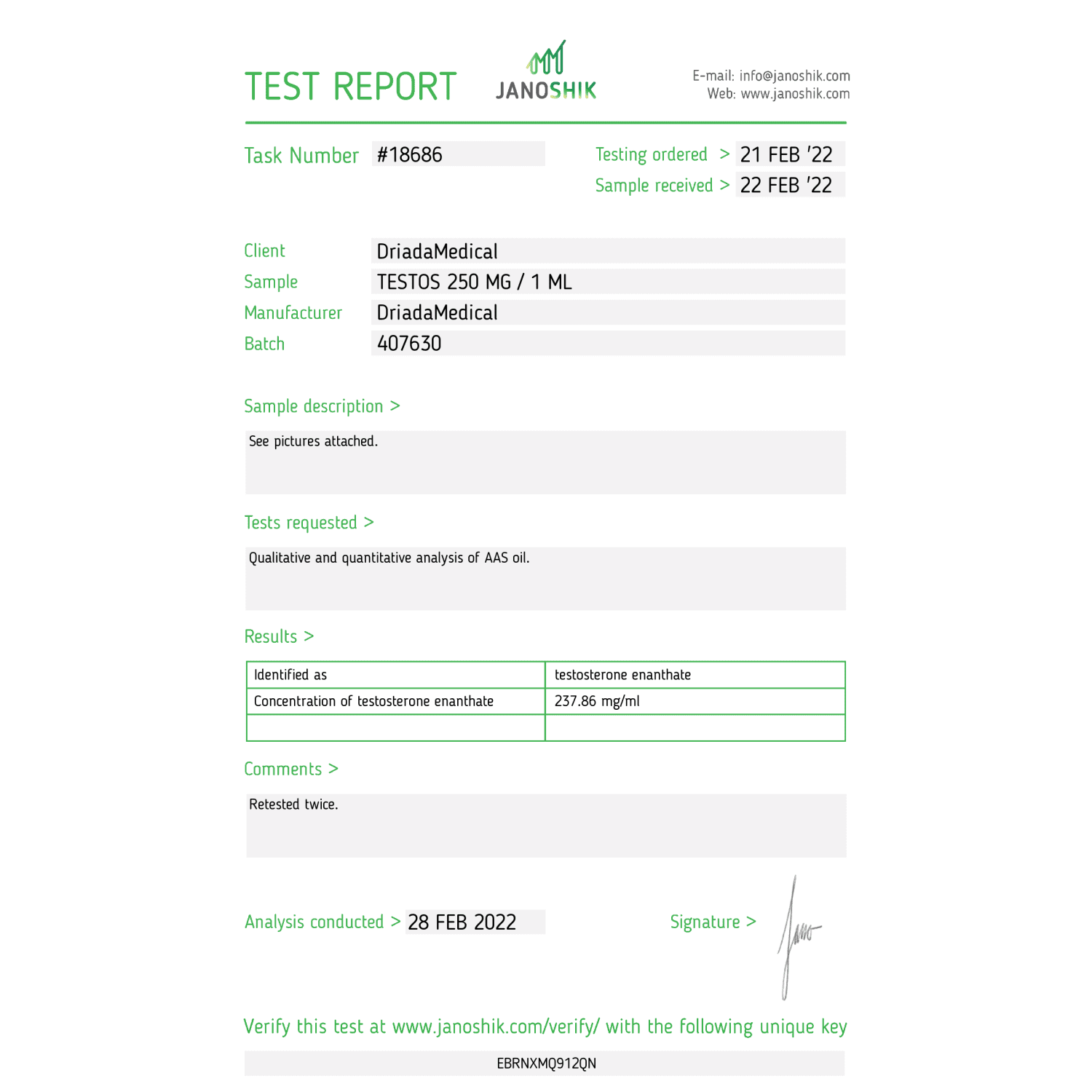
Testos (Testosterone Enanthate) Driada Medical 250 mg/ml
€ 55,00
- Active ingredient: Testosterone enanthate
- Type: Anabolic steroid (testosterone derivative)
- Packaging: 10 x 1 ml
- Form: Injections
- Carrier oil: Grapeseed oil
Testos 250 mg/ml (Testosterone Enanthate)
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone in humans and plays a crucial role in the development of reproductive tissues such as the testes and prostate in men, as well as in women. It also promotes secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass and body hair growth in men. Testosterone is involved in overall health, well-being, and the prevention of osteoporosis in both sexes. Insufficient testosterone levels in men can lead to conditions such as bone fragility and loss. Furthermore, testosterone has pronounced anabolic properties, including increased muscle mass, accelerated protein synthesis, improved recovery, and improved glycogen storage in muscles. Testosterone controls numerous processes in the body, making it the most common and essential hormone for various purposes. It is used not only by older individuals with age-related hypogonadism, but also by athletes during steroid cycles as a key compound.
Action mechanism
Testosterone binds to androgen receptors and serves as a precursor to dihydrotestosterone, another biologically active androgen formed through the conversion of testosterone by the enzyme 5α-reductase. Dihydrotestosterone has a fivefold greater affinity for androgen receptors. These hormones induce changes in the receptor structure, transmitting signals to the cell nucleus, where androgenic effects are achieved by modifying the activity of specific DNA genes. Testosterone can also convert to estrogen through aromatase activity, primarily to estrogen, which activates feedback through the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis and suppresses endogenous testosterone secretion when exogenous testosterone is administered.
Medical use
Testosterone is included on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, underscoring its importance as a medication in primary health care systems. It is used to treat gender dysphoria, male hypogonadism, and some types of breast cancer. As testosterone levels decline with age, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) becomes necessary to maintain health and quality of life. HRT maintains serum testosterone levels within the normal range. The decline in testosterone production due to aging has led to increased interest in androgen replacement therapy. Testosterone plays a role in mood, spatial ability, attention, memory, and other cognitive functions in humans. Early evidence suggests that low testosterone levels are a risk factor for cognitive decline, including Alzheimer’s disease.
In both men and women, testosterone contributes to overall health, well-being, and the prevention of osteoporosis. In men, insufficient testosterone levels can lead to frailty, bone loss, and sexual dysfunction. Therefore, testosterone treatment is beneficial for adult men with age-related low testosterone levels who experience sexual dysfunction.
Testosterone for seniors
Men over 35 who report reduced well-being are often advised to undergo a testosterone blood test. If their levels fall below 12 nmol/L, they may be advised to undergo hormone replacement therapy. This decision offers several positive aspects. It improves body composition, increasing muscle mass and reducing fat. Sexual function is rejuvenated, and a certain anti-aging effect is observed, reversing the negative effects of androgen deficiency. However, it is essential to consult a doctor and regularly monitor lipid profiles, general blood parameters, estradiol levels, and prolactin.
It’s equally important to note that natural gonadotropin production steadily approaches zero with HRT. Therefore, if you want to maintain fertility, special therapy involving gonadotropins is necessary.
The dosage of testosterone therapy should be chosen in consultation with a doctor. Dosage depends on the individual’s normal testosterone levels, current levels, body weight, body fat percentage, sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels, and aromatization status.
Approximate dosages for replacement therapy are significantly lower than those used by athletes, ranging from 50 to 200 mg per week.
Testosterone in sport
Testosterone’s main benefit is its ability to increase muscle mass and strength. It has both anabolic and androgenic effects. Androgens enter cells and interact with androgen receptor (AR) proteins. This interaction causes a change in the shape of the AR protein, activating it. Although this change is minimal, it allows the AR to enter the nucleus and bind to DNA, initiating gene transcription.
The rapid weight gain associated with testosterone is attributed to significant water retention due to sodium retention and estrogenic effects. Testosterone can help alleviate joint problems, pain, and creaking in the shoulders and knees, although nandrolone and growth hormone are often preferred in this regard. Testosterone stimulates the body’s regeneration processes, improves overall vitality and motivation for exercise, and prevents overtraining. It also increases oxygen capacity and nitric oxide production, leading to improved congestion during training sessions.
The recommended dosage in sports ranges from 250 to 500 mg per week, with an increase proportional to the athlete’s body weight. Testosterone cycles typically last 8 to 10 weeks, followed by post-cycle therapy after 2–3 weeks. Testosterone is often used for extended periods. In high-level professional athletes, the maximum dose is 2000 mg per week, as further increases would be ineffective and would only increase the risk of side effects.
To prevent the development of estrogenic side effects resulting from the aromatization process, it is highly recommended to test for and use aromatase inhibitors. It is best to test estradiol levels before and during use of aromatase inhibitors to monitor efficacy and determine the necessary dose. Consulting a professional when choosing a dosage is highly recommended, and the information provided below is for reference purposes only.
Dosages
- Beginners: 250 mg per week
- Average dosage: 300-750 mg per week
- High dosage: 750+ mg per week
Effects
- Increased muscle mass
- Development of male genitalia and secondary sexual characteristics (e.g., deep voice, masculine facial features, male-pattern hair growth)
- Promotion of spermatogenesis and male behavior (e.g., sexual desire, aggression, decisiveness)
- Burn fat
- Increased strength
- Increased libido
- Reduction of blood cholesterol levels
- Reduction of the risk of cardiac ischemia and coronary heart disease
- Stimulation of erythropoiesis and distribution of male-type subcutaneous adipose tissue
- Influence on nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism
Side effects
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased sexual behavior
- Hemoconcentration (increased blood clotting)
- Possibility of blood clots forming in the arteries and veins
- Water retention (edema)
- Masculinization
- Aggression, agitation, irritability
- Alopecia (baldness of the scalp)
- Acne
- Insomnia (rare)
Profile
- Half-life: 4-5 days
- Injection frequency: 4-7 days
Pharmaceutical form
- Oily solution for intramuscular injection
Contraindications
- Pregnancy
- Known or suspected prostate or breast cancer
- Breastfeeding
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients
Conservation
- Do not use after the expiration date
- Store between 8°C and 30°C
- Do not freeze
- Protect from light










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.