Testosterone Undecanoate
€ 50,00
- Active ingredient: Testosterone Undecanoate
- Type: Anabolic steroid (testosterone derivative)
- Packaging: 10 x 1 ml
- Form: Injectable
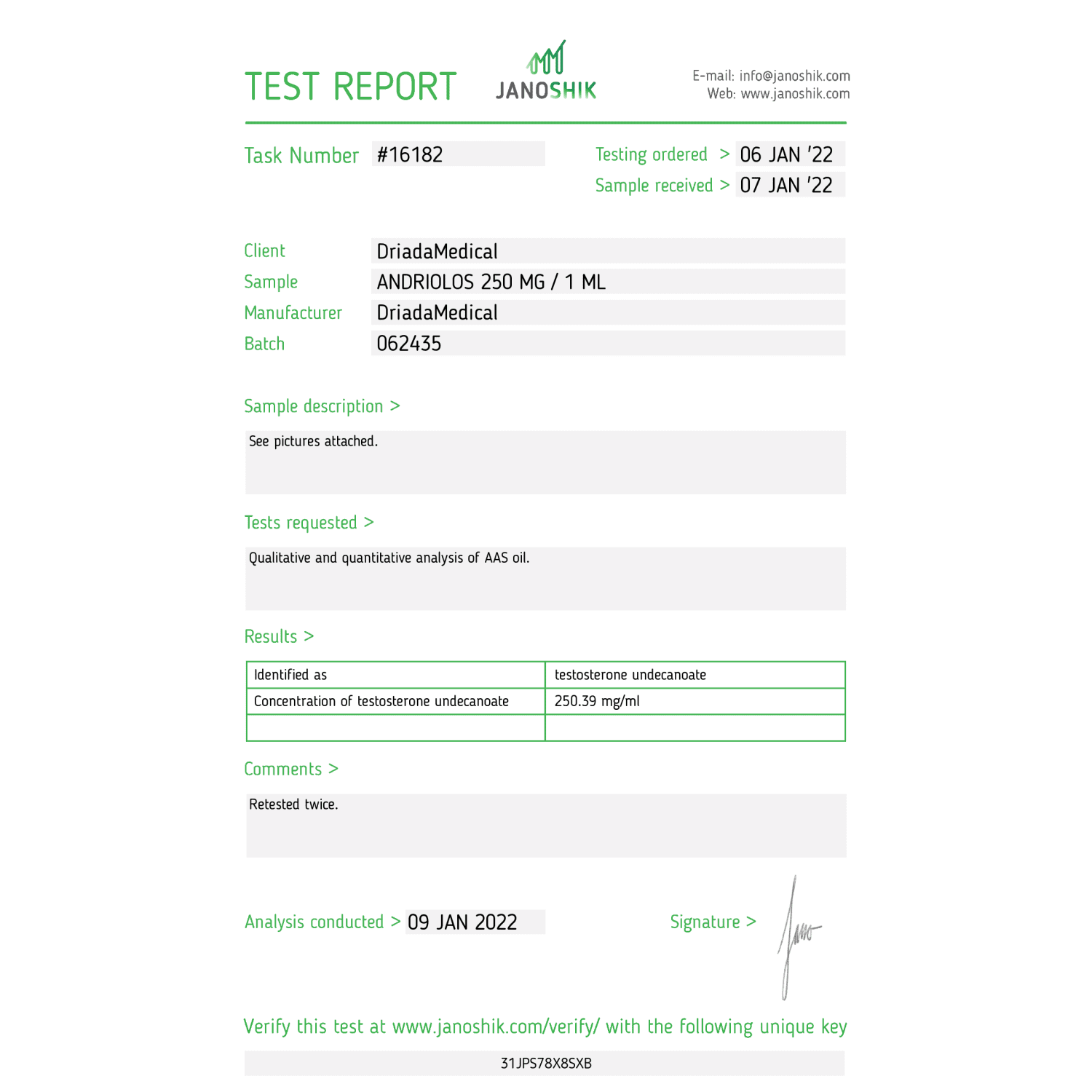
Andriolos 250 mg/ml (Testosterone Undecanoate)
Testosterone is a primary sex hormone present in both men and women. It plays a crucial role in the development of reproductive tissues, such as the testes and prostate, and promotes secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass and body hair growth in males. It also contributes to overall health, well-being, and the prevention of osteoporosis. Insufficient testosterone levels in men can lead to abnormalities, including bone fragility and loss. Testosterone has pronounced anabolic properties, such as increasing muscle mass, accelerating protein synthesis, improving recovery, and increasing muscle glycogen supply. It regulates numerous processes in the body and is considered one of the most important hormones, used in hormone replacement therapy for aging individuals and as a base compound in steroid cycles for athletes.
Mechanism of action
Testosterone binds to androgen receptors and serves as a precursor to dihydrotestosterone, a biologically active androgen formed by the action of the enzyme 5α-reductase on testosterone. Dihydrotestosterone has a fivefold greater affinity for androgen receptors. Binding of these hormones to androgen receptors causes structural changes in the receptor, transmitting a signal to the cell nucleus. This activation leads to androgenic effects by influencing the activity of specific DNA genes. Testosterone can also be converted to estrogen through the process of aromatization. Estrogen, rather than testosterone, primarily activates feedback through the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis, suppressing endogenous testosterone secretion when exogenous testosterone is administered.
Medical use
Testosterone is included on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines due to its importance in maintaining overall health. It is used medically to treat conditions such as gender dysphoria, male hypogonadism, and some types of breast cancer. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) or hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often prescribed for men with age-related low testosterone levels to maintain their health and quality of life. The decline in testosterone production with age has sparked interest in androgen replacement therapy. Testosterone also plays a role in cognitive function, and low testosterone levels have been associated with cognitive decline and possibly Alzheimer’s-type dementia.
Testosterone for seniors
Men over 35 who experience reduced well-being are often advised to monitor their testosterone levels. If levels fall below 12 nmol/L, testosterone replacement therapy may be recommended. This decision offers several benefits, including positive changes in body composition, such as increased muscle mass and reduced fat. It can revitalize sexual function and overall vitality. However, careful monitoring of lipid profiles, clinical blood parameters, estradiol levels, and prolactin levels is crucial. Furthermore, natural gonadotropin production decreases with hormone replacement therapy, so specific therapy with gonadotropins may be necessary for those seeking to conceive.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional when selecting the right dosage for testosterone therapy. The appropriate dosage depends on individual factors such as normal testosterone levels, current levels, body weight, body fat percentage, sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels, and aromatization. Dosages for replacement therapy are typically much lower than those used by athletes, ranging from 50-200 mg per week.
Testosterone in sport
The main benefit of testosterone in sports is its ability to increase muscle mass and strength. It exerts significant anabolic effects and has a notable androgenic effect. Androgens enter cells and interact with androgen receptor (AR) proteins, causing them to change shape and activate. This activation allows the AR to enter the nucleus and bind to DNA, influencing gene expression. Testosterone also promotes water retention, leading to rapid weight gain and improved joint health. It enhances regeneration processes, overall energy levels, and blood oxygen capacity, resulting in satisfactory muscle congestion during training.
The recommended dosage in sports is typically 250-500 mg per week, adjusted based on the athlete’s body weight. Testosterone cycles typically last 8-10 weeks, followed by post-cycle therapy after 2-3 weeks. Some athletes may use testosterone for longer periods, but dosages should not exceed 2,000 mg per week due to diminishing returns and increased side effects. To minimize estrogenic side effects resulting from aromatization, it is advisable to undergo testing and consider the use of aromatase inhibitors. Dosage selection should be left to professionals, and the information provided below is for reference purposes only.
How to use
Testosterone undecanoate is not widely used in strength sports due to its undefined and insufficient effect and long-lasting action. However, it is commonly used in clinical andrology as hormone replacement therapy for patients with age-related androgen deficiency. Testosterone undecanoate’s long half-life allows for less frequent injections to maintain stable blood testosterone levels. After an initial loading dose, injections can be administered every 3 months at 6-week intervals, although more frequent administration every 4–5 weeks is often preferred.
Pharmacokinetic studies have shown that testosterone levels return to the physiological range within 3 days of the first administration. With an interval between injections of approximately 10–12 weeks, testosterone concentrations consistently remain within the normal range. The initial dosing interval can be shortened to six weeks to achieve stable testosterone levels more quickly.
It is important to follow these recommendations for the administration of testosterone undecanoate:
- Administer the first and second doses of testosterone undecanoate 4-6 weeks apart.
- Subsequently, maintain an interval between injections of approximately 10-12 weeks.
Effects
- Increased muscle mass
- Development of male genitalia and secondary sexual characteristics
- Spermatogenesis and improvement of male behavior (sexual, aggressive, decisive)
- Fat burning
- Increased strength
- Libido stimulation
- Reduction of blood cholesterol levels
- Reduction of the risk of cardiac ischemia and coronary heart disease
- Stimulation of erythropoiesis and influence on male-like subcutaneous adipose tissue distribution
- Influence on nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism
Side effects
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased sexual behavior
- Hemoconcentration (blood clotting)
- Potential for blood clots in arterial and venous vessels
- Water retention (edema)
- Masculinization
- Aggression, agitation, irritability
- Alopecia (baldness of the scalp)
- Acne
- Insomnia (rare)
Profile
- Half-life: 28-34 days
- Frequency of injections: 7-14 days
Pharmaceutical form
- Oily solution for intramuscular injection.
Contraindications
- Pregnancy
- Known or suspected prostate or breast cancer
- Breastfeeding
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any excipients
How to store
- Do not use after the expiration date
- Store between 8º and 30ºC
- Avoid freezing
- Protect from light









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.